Running a Private GemServer inside the Firewall
rubygems.org has made it so easy to publish a gem for the world to use but what do you do when your gem is proprietary and you only want to publish it within your company?
This is something I’ve just been through at my company and thought I’d share the steps I went through. We need to
- Setup an inside-the-firewall gem server
- Configure our gems to deploy to it
- Configure our apps to use it
Setup an inside-the-firewall gem server
The first thing you have to decide is what gemserver to use. Rubygems.org has a helpful page called running your own gemserver that basically lists 3 choices in a goldilocks situation.
-
too small - gem server is a command built into rubygems
This works but you need to log onto the server to install a new gem and it serves all gems on the system not just your proprietary ones
-
too big - rubygems.org is open source so we could deploy it on our own server
This seems pretty complex to setup and even they tell you to “consider checking out Geminabox”
-
just right - gem in a box is a simple sinatra app to allow you to host your own in-house gems
This is easy to setup, has a web interface and supports a command line to remotely publish new gems.
geminabox is what I decided to go with.
The readme on github describes the server setup for geminabox and it just worked. The only thing to keep in mind is that you cannot use bundler as then you will only serve the gems in the bundle instead of the gems you publish. I spent some time adding bundler before realizing that was a bad idea and backing it out.
Once geminabox is up and running you can view your gems at your internal url and you’ll see the gem server homepage showing you it has no gems.
The easiest thing is to add a new gem by clicking “Upload Another Gem” and selecting a .gem file from your hard drive
(I picked diagnostics-0.0.1.gem in the image below).
Once you click uppload you should see your gem on the page.
At this point we could start using this gem server in our apps but before we talk about that let’s automate the manual process we just went through to add a gem.
Configure our gems to deploy to the gem server
I’ve been using bundler to create my gems with the bundle gem command and one of the features that gives you is a set of nice rake tasks.
Check out the New Gem with Bundler Railscast to learn how it works.
$ bundle gem my_awesome_gem
create my_awesome_gem/Gemfile
create my_awesome_gem/Rakefile
create my_awesome_gem/.gitignore
create my_awesome_gem/my_awesome_gem.gemspec
create my_awesome_gem/lib/my_awesome_gem.rb
create my_awesome_gem/lib/my_awesome_gem/version.rb
Initializating git repo in /Users/alex/my_awesome_gemLet’s look at the tasks we’ve got.
$ cd my_awesome_gem
$ rake -T
rake build # Build my_awesome_gem-0.0.1.gem into the pkg directory
rake install # Build and install my_awesome_gem-0.0.1.gem into system gems
rake release # Create tag v0.0.1 and build and push my_awesome_gem-0.0.1.gem to Rubygemsrake build and rake install do their work locally but rake release is what you call when you’re done and ready to release your gem into the wild.
This task will push your changes to github, create a git tag,
build your gem package and deploy it to http://rubygems.org.
We need to do something to change that last part so it deploys to our private gem server instead of rubygems.org.
Let’s spend some time looking into bundler to figure out how rake release works.
The magic all happens inside a file lib/bundler/gem_helper.rb
* It defines a :release rake task
* Which calls release_gem
* Which calls [rubygem_push] (https://github.com/carlhuda/bundler/blob/1-0-stable/lib/bundler/gem_helper.rb#L72-79)
* Finally this will call gem push pkg/my_awesome_gem-0.0.1.gem which pushes to http://rubygems.org. We’ve found the behavior we need to change.
geminabox adds a custom rubygems command called inabox so you can deploy a gem with the command gem inabox pkg/my-awesome-gem-1.0.gem.
Unfortunately bundler does not seem to have a convenient way to change this so we’re going to monkey patch bundler Bundler::GemHelper#rugygem_push
method to use the geminabox command instead. (please let me know if you have a better idea)
We’ll add our monkey patch to our Rakefile since its called by a rake command.
# Rakefile in your my_awesome_gem gem
# Monkey patch Bundler gem_helper so we release to our gem server instead of rubygems.org
module Bundler
class GemHelper
def rubygem_push(path)
gem_server_url = 'http://gems.intranet.mycompany.com'
sh("gem inabox '#{path}' --host #{gem_server_url}")
Bundler.ui.confirm "Pushed #{name} #{version} to #{gem_server_url}"
end
end
endYou can see this will call gem inabox ... so we also need to add geminabox to our gem’s bundle. We do this in the .gemspec as a development dependency
# my_awesome_gem.gemspec in your gem
Gem::Specification.new do |s|
.. lots of other stuff ...
s.add_development_dependency "geminabox"
endNow when we call rake release it will push the gem to our private server instead of the public one. Let’s see:
$ rake release
my_awesome_gem 0.0.1 built to pkg/my_awesome_gem-0.0.1.gem
Tagged v0.0.1
Pushed git commits and tags
Pushed my_awesome_gem 0.0.1 to http://gems.intranet.mycompany.comNow when we go to the gem server site, we can see our new awesome gem in the list
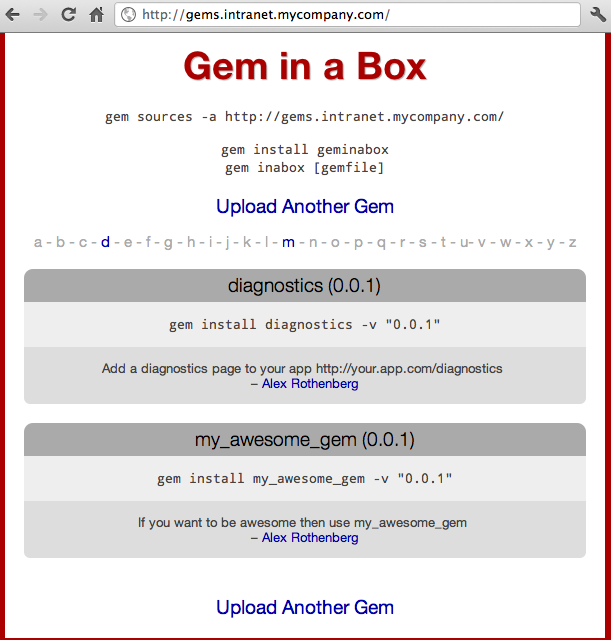
The gem is there an you can use install it with a command like gem install my_awesome_gem --source http://gems.intranet.mycompany.com
Using your Gem Server from an application
We’ve just seen how we can use the source option to tell rubygems where to look when installing our gem by hand,
but in a modern application we all use bundler and a Gemfile to manage our gems so
how do we tell bundler to user our private gemserver for our private gems?
Its super simple, you just need to add a source to the top of your Gemfile
source "http://gems.intranet.mycompany.com/"
source :rubygems
# regular old gems come from rubygems.org
gem "rails"
gem "rack"
gem "haml"
# my private gem comes from my private gemserver
gem 'diagnostics'Now when we run bundle it looks in our private gem server as well as the public rubygems.org.
Now that that you’ve got my_awesoem_gem you’re ready to add awesomeness to your app.
$ bundle
Fetching source index for http://gems.intranet.mycompany.com/
Fetching source index for http://rubygems.org/
Using rake (0.9.2)
Using activesupport (3.1.0)
Installing my_awesome_gem (0.0.1)
...etc..